1. What is Shell?
- Shell: A command interpreter and programming environment
- 用户和操作系统之间的接口
- 作为核外程序而存在
| 用户和操作系统之间的接口 | 作为核外程序而存在 |
|---|---|
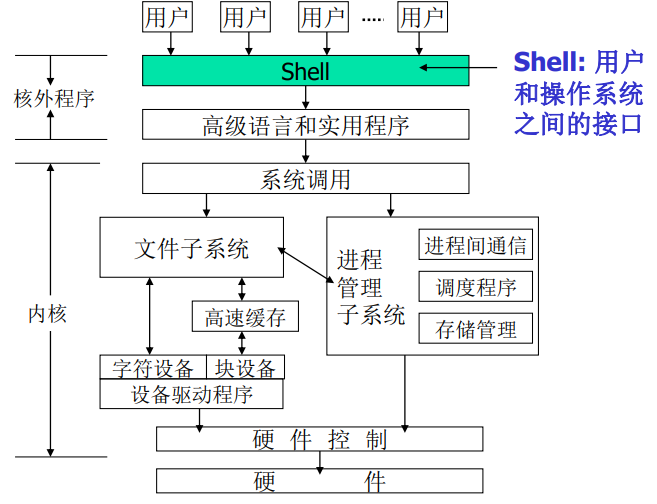 |
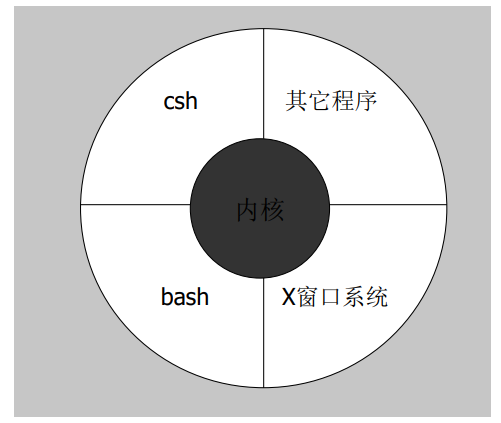 |
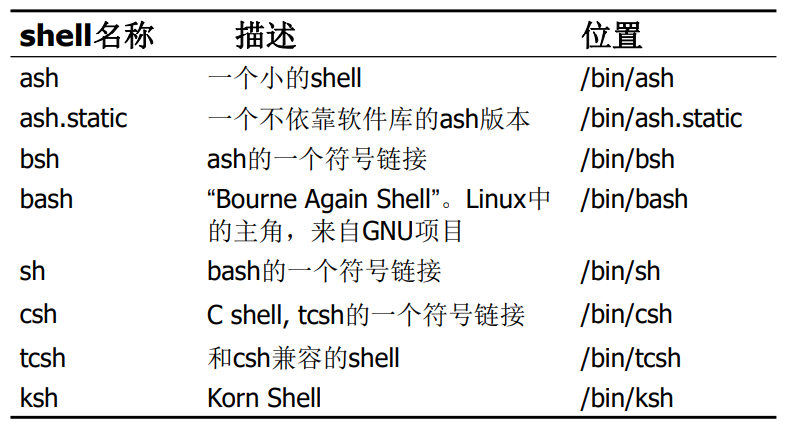
1.1 各种不同的Shell
1.2 Shell 的双重角色
- 命令解释程序
- Linux的开机启动过程;进程树
- Shell的工作步骤:打印提示符;得到命令行;解析命令;查找文件;准备参数;执行命令
- 独立的程序设计语言解释器
- KISS (Keep It Small and Stupid)
- Reusable tools
- Redirection and pipe
2. 脚本
2.1 使用命令行
脚本是能在命令行直接输入的,但仅会执行一次

2.2 编写脚本文件
脚本文件
- 注释
- 退出码(exit code)

2.3 执行脚本文件
方法一:
1 | |
方法二:
1 | |
方法三:
1 | |
方法一二原理相同:新启bash进程执行脚本
方法三使用当前bash进程执行脚本
2.4 用户环境
.bash_profile,.bash_logout,.bashrc files
.bash_profile: 用户登录时被读取,其中包含的命令被bash执行.bashrc: 启动一个新的shell时读取并执行.bash_logout: 登录退出时读取执行
Alias
- alias/unaliascommand
环境变量
export command
export, env & set command
3. 变量
3.1 用户变量
用户变量:
- 用户在shell脚本里定义的变量
变量的赋值和使用
var=valueecho $var
read命令
用法:
read var或readREPLY variable
引号的用法
双引号,单引号
转义符
\
=两侧不能加空格
变量没有类型,或者可以认为是字符串
Read用法
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
引号的用法
单引号内的所有字符都保持它本身字符的意思,而不会被bash进行解释,例如,\$就是\$本身而不再是bash的变量引用符;\就是\本身而不再是bash的转义字符。
除了$、``(不是单引号)和 外,双引号内的所有字符将保持字符本身的含义而不被bash解释
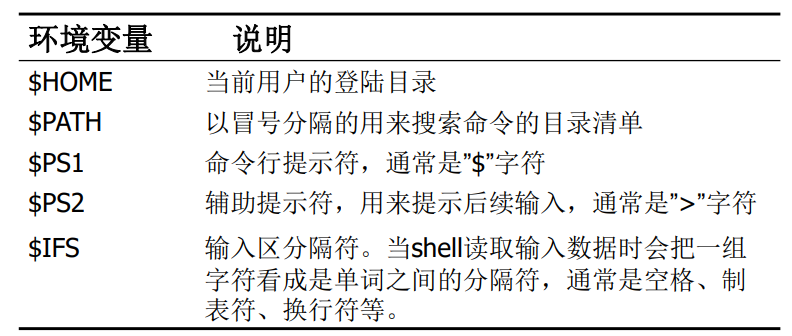
3.2 环境变量
Shell环境提供的变量。通常使用大写字母做名字
3.3 参数变量和内部变量
调用脚本程序时如果带有参数,对应的参数和额外产生的一些变量。

4. 语句
4.1 条件测试
退出码
test命令:test expression 或 [ expression ]
test命令支持的条件测试
- 字符串比较
- 算术比较
- 与文件有关的条件测试
- 逻辑操作
字符串比较

算术比较
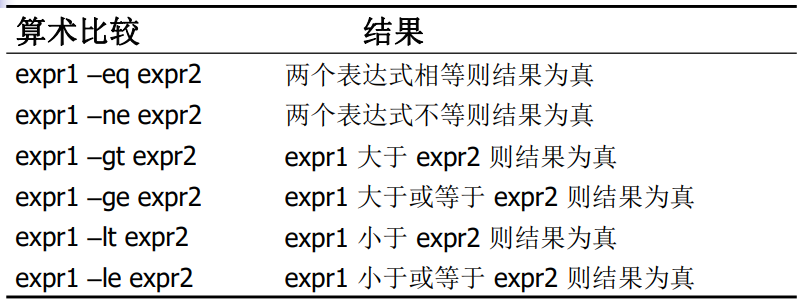
与文件有关的条件测试
逻辑操作

4.2 if语句
1 | |
- 紧凑模式:使用 ; 分割
1 | |
4.3 case语句
- 双分号
1 | |
1 | |
4.4 for语句
- 适用于对一系列字符串循环处理
1 | |
1 | |
4.5 while语句
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
$(())整数运算,否则会看作字符串
不推荐使用 until
4.6 select语句
生成菜单列表
1 | |
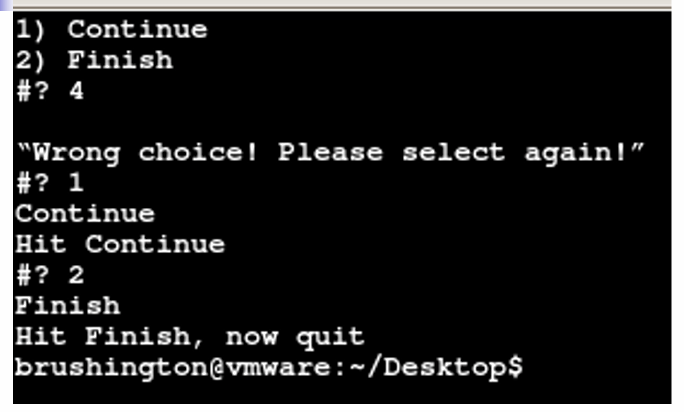
4.7 命令表和语句块
命令表
命令组合
分号串联:command1 ; command2 ; …
AND命令表(&&): 前面成功才会执行后面的命令
OR命令表(||): 前面失败才会执行, 可用作备用命令
{statement1; statement2 ; … ;} 会看做一个命令
语句块
1 | |
4.8 函数
定义时不带参数
1 | |
- 局部变量: local关键字
- 函数的调用: func para1 para2 …
- 返回值: return
例子


5. 其他
5.1 杂项命令
- break: 从for/while/until循环退出
- continue: 跳到下一个循环继续执行
- exit n: 以退出码”n”退出脚本运行
- return: 函数返回
- export: 将变量导出到shell,使之成为shell的环境变量
- set: 为shell设置参数变量
- unset: 从环境中删除变量或函数
- trap: 指定在收到操作系统信号后执行的动作
- “:”(冒号命令): 空命令
- “.”(句点命令)或source: 在当前shell中执行命令
5.2 捕获命令输出
$(command) 或 `command`
$PWD 与 $(pwd)
5.3 算术扩展

5.4 参数扩展
问题:批处理 1_tmp, 2_tmp, …
方法:
1 | |
参数扩展更复杂的形式

5.5 即时文档
在shell脚本中向一条命令传送输入数据
例如: 输入 !CATINPUT! 才会停止
1 | |