软件系统设计-架构(1) 概述
1. 课程背景
1.1 为什么要研究软件设计与架构?Why Study Software Design & Architecture?
- 软件(IT)系统无处不在
Software(IT) systems are everywhere - 每个软件密集型系统都有一个软件设计和架构
Every software intensive system has a sofftware design and architecture - 软件设计和架构是实践,教育和研究中越来越重要的领域
Software design and architecture are an increasingly important area of practice, education, and research - 专业: 软件架构师
As a profession: Software Architect - 作为研究领域 As a research area
- 最初于1960年左右开始 Originally started around 1960
- 自1990年以来备受关注 Attracting major attention since 1990
- 本课程是关于
- 软件设计和架构的概念,原理,方法和模式
Concepts, principles, methods, and patterns of software design and architecture - 软件设计和架构的最新实践
State-of-the-art practices of software design and architecture
- 软件设计和架构的概念,原理,方法和模式
1.2 学习目标 Learning Objectives
- 理解软件设计和架构的概念和原理
Understand concepts and principles of software design and architecture - 通过考虑需求或通过反向架构来创建软件架构
Create software architecture by taking requirements or through reverse architecting - 在创建软件架构和设计的时候应用设计模式、风格、中间件技术和框架
Apply patterns, styles, middleware technologies and frameworks in creating software architecture and design - 分析软件设计和评估软件架构的系统性
Analyze software design and evaluate software architecture systematically - 了解应用在软件设计和架构中的最先进的方法
Understand state-of-the-art methods applied in software design and architecture - 理解软件设计与软件架构之间的关系,以及其他软件工程的领域话题
Understand relationships between software design and software architecture, and other software engineering topic areas
2. 介绍
2.1 理解软件工程 Understanding Software Engineering
- Software 和 Engineering
- Software vs. Hardware
- 软件是不可见的: 软件是虚拟的,而硬件是实体的。
- 软件制作出来就是为了被修改和改变的(软件的演化是他的本质属性)
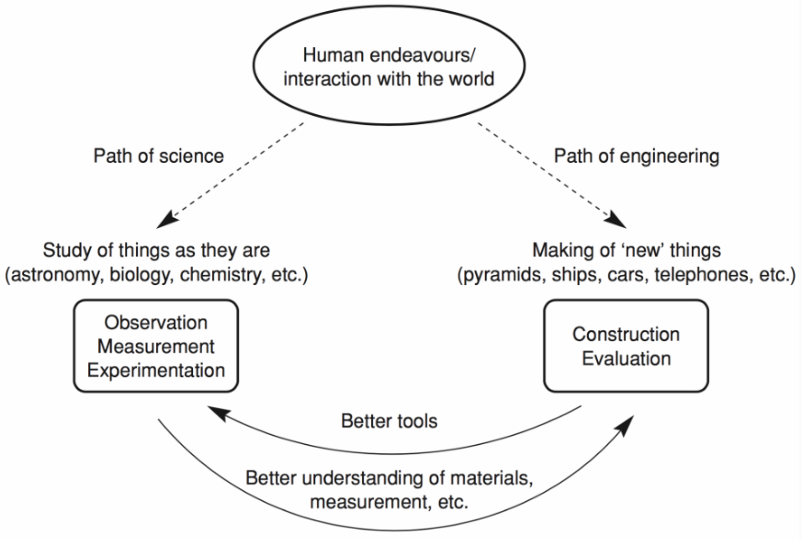
- Science vs. Engineering: 科学的研究是研究这个世界既有的部分,而工程是研究的是人类创造新的世界(是不是因为人才产生的),下面的图是很重要的。
2.2 什么是软件架构 What is Software Architecture
- 定义1: 程序或计算系统的软件架构是系统的一个或多个结构,它包括软件元素、这些元素的外部可见属性以及它们之间的关系。
Definition 1: “The software architecture of a program or computing system is the structure or structures of the system, which comprise software elements, the externally visible properties of those elements, and the relationships among them.” [Software Engineering Institute (SEI)] - 定义2: 系统的基本组织,体现在其组件,它们之间的相互关系以及环境以及支配其设计和演进的原则。
Definition 2: “The fundamental organization of a system, embodied in its components, their relationships to each other and the environment, and the principles governing its design and evolution.” [IEEE 1471 -2000 “Recommended Practice for Architectural Description of Software-Intensive Systems”]
Module和Component的区别
- Component(组件): 是已经实现了的软件部分
- Module(模块): 是还没有实现出来的软件部分
- Element包含了Component和Module。
2.3 架构 vs. 设计 Architecture vs. Design
架构是关于软件设计 It’s about software design
- 所有的架构都是软件设计,但不是所有的软件设计都是架构
All architecture is software design, but not all design is software architecture - 架构是设计过程的一部分
“Architecting” is part of the design process
- 所有的架构都是软件设计,但不是所有的软件设计都是架构
其他观点 Other views
架构是更高层的设计 High-level designs
架构是设计决策的组合 A set of design decisions
架构是根据不同项目而不同的 Locality
系统的结构或组织 Structure/Organization of the system
- 元素(Elements): 组件(Components)和连接件(Connectors)
Elements: components & connectors - 关系: 静态(static)和动态(dynamic)的关系
Relationships: static & dynamic relationships
- 元素(Elements): 组件(Components)和连接件(Connectors)
属性: 元素,元素组和整个系统
Properties: elements, groups of elements & overall system
2.4 架构 vs. 结构 Architecture vs. Structure
- 架构将系统分解成组件/模块/子系统,降低每一部分的复杂度
Decomposition of system into components/modules/subsystems - 架构定义 Architecture defines
- 组件接口: 组件可以做什么?
Component interfaces: What a component can do? - 组件交流和依赖: 组件可以怎么沟通交流?
Component communications and dependencies: How components communicate? - 组件职责: 当我们询问它时,组件需要精确的知道自己将要做什么?
Component responsibilities: Precisely what a component will do when you ask it?
- 组件接口: 组件可以做什么?
2.4.1 结构和架构 Structure and Architecture
| 结构 | 架构 |
|---|---|
 |
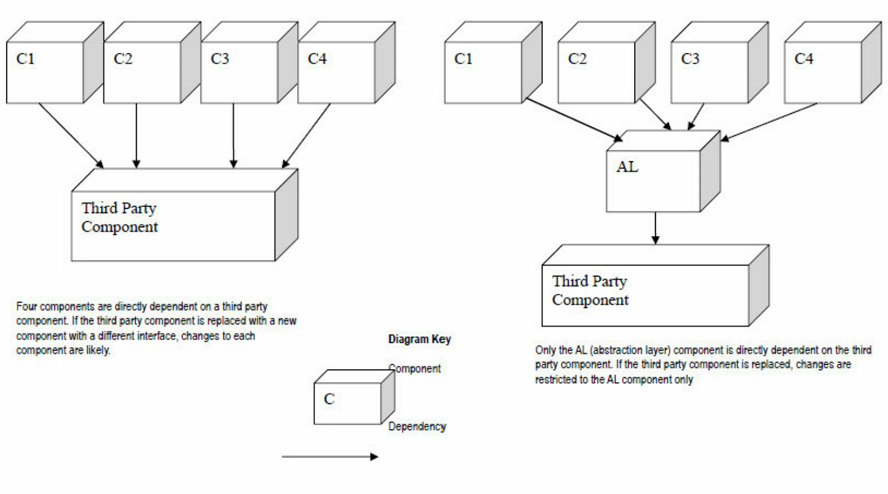 |
图中左侧的设计: 第三方的模块与其他的四个模块直接耦合
图中右侧的设计: 我们加入了AL模块来屏蔽了变化
2.4.2 架构确定通信 Architecture Specifies Communication
通信涉及 Communication involves:
- 数据通过机器传递 Data passing mechanisms, for example:
- 函数调用 Function call
- 远程方法调用 Remote method invocation
- 异步信息 Asynchronous message
- 控制流 Control flow
- 组件间的信息流来实现需要的功能 Flow of messages between components to achieve required functionality
- 序列化的 Sequential
- 并发/并行 Concurrent/parallel
- 同步 Synchronization
2.4.3 架构强调非功能性需求(NFA) Architecture Address NFRS
- 非功能性需求(Non-functional requirements)定义了系统运行的有多好
Non-functional requirements (NFRs) define “how well a system works?” - 当然也需要考虑功能性需求。
- 非功能性需求很少在功能性需求中被发现
NFRs rarely captured in functional requirements- 又名架构需求 Aka. architecture requirements
- 必须通过架构引出 Must be elicited by architect
- 非功能性需求包括 NFRs include
- 技术约束 Technical constraints
- 商业约束 Business constraints
- 质量属性 Quality attrilbutes
- 讨论: 质量属性列表 Discussion: A list of quality attributes?
3. 如何创建一个设计 How to Develop a Design?
广义的设计策略 Generic Design Strategies:
- 分解 Decomposition
- 抽象 Abstraction
- 逐步的: 分而治之 Stepwise: Divid and Conquer
- 生成和测试 Generate and Test
- 迭代: 渐进式细化 Iteration: Incremental Refinement
- 重用元素 Reuseable elements
3.1 设计是一种抽象 Design is an Abstraction
- 架构提供了设计的更高层抽象视角
Architecture provides an higher level abstract view of a design- 隐藏设计的复杂性和实现
Hides complexity and implementation of design - 可能是或者可能不是架构元素和软件元素之间的直接映射
May or may not be a direct mapping between architecture elements and sottware elements
- 隐藏设计的复杂性和实现
- 黑盒设计 和 白盒设计 Blackbox design and Whitebox design
- 是对系统结构和交互的非正式描述
Informal depiction of system’s structure and interactions. - 描述在架构中内嵌的设计哲学
Portray the design philosophies embodied in the
architecture
- 是对系统结构和交互的非正式描述
- 讨论: 为什么在设计中使用抽象?Discussion: Why abstraction in design?
3.2 架构视图 Architecture Views
- 架构视图主要是为了应对软件不可见的问题,屏蔽其他没有影响的部分,将关注点进行分离
- 软件架构代表了一个复杂的设计制品
A software architecture represents a complex design artifact - 很多架构的可能视图: 类比建筑-平面图,外部设计,电力设计,水暖,空气调节
Many possible ‘views’ of the architecture: Analogy with buildings-floor plan, external, electrical, plumbing, air-conditioning
3.2.1 P.Krutchen的4+1视图模型 P.Krutchen’s 4+1 View Model
- 逻辑视图: 描述了架构中重要的架构元素以及它们之间的关系
Logical view: describes architecturally significant elements of the architecture and the relationships between them. - 过程视图: 描述了架构中的并发和通信元素
Process view: describes the concurrency and communications elements of an architecture. - 物理视图: 描述了主要进程和组件是如何映射到应用程序硬件上的
Physical view: depicts how the major processes and components are mapped on to the applications hardware. - 开发视图: 描述了软件组件是如何在软件内部组织的,比如配置管理工具
Development view: captures the internal organization of the software components as held in e.g./ a configuration management tool. - 用例场景: 捕获架构需求,与多个特定视图相关
Architecture use cases: capture the requirements for the architecture; related to more than one particular view- 四个视图在某一个场景下进行描述
4. 架构师和软件架构师 Architect & Software Architect
架构师设计了满足人类需求的结构
Architects design structures to meet human needs. - James Fitch, 1972
- 架构师的角色保持不变 The role of the architect remains the same
- 倾听用户,理解整体的需求
Listening to clients, understanding the totality of needs - 审查可行性
Scrutinizing feasibilities - 形成结构的实用愿景并创建蓝图
Forming a practical vision of a structure and creating a blueprint - 监督构建过程,保证是符合计划的
Overseeing construction and ensuring compliance to the plan - 引导在暴风雨式的设计变更、危机和歧义性中的愿景
Guiding the vision through the tempest of design changes, crises and ambiguities
- 倾听用户,理解整体的需求
- 软件架构师监督软件构建专业人员: 开发人员、工程师和设计者
Software architects oversee software construction professionals: Programmers, Engineers, Designers - 有名的软件架构师
- Bill Gates: Chief Software Architect of Microsoft
- Tim Bernrs-Lee: Inventor and Chief Architect of World Wide Web
- Roy Fielding: Representational State Transfer (REST)
4.1 软件架构师做什么? What Does a Software Architect Do?
- 联络 Liaison
- 在客户、技术团队和商业/需求分析师之间
Among clients, technical team and business/requirements analysts - 与管理或营销 With management or marketing
- 在客户、技术团队和商业/需求分析师之间
- 软件工程: 软件工程的最佳实践
Software Engineering: Software engineering best practices - 技术知识: 深入理解技术领域
Technology Knowledge: Deep understanding of technology domain - 风险管理: Risk Management
- 与设计、技术决策相关的风险
Risks associated with the design, technology choices - More?
- 与设计、技术决策相关的风险
5. 总体设计模型 A General Design Model
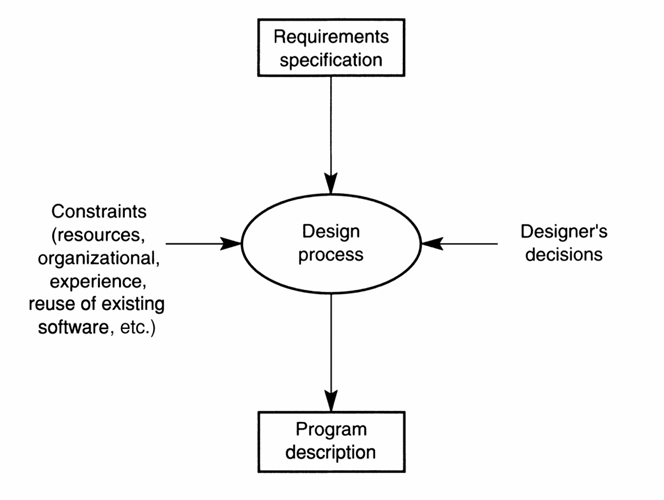
开发和设计是在做减法
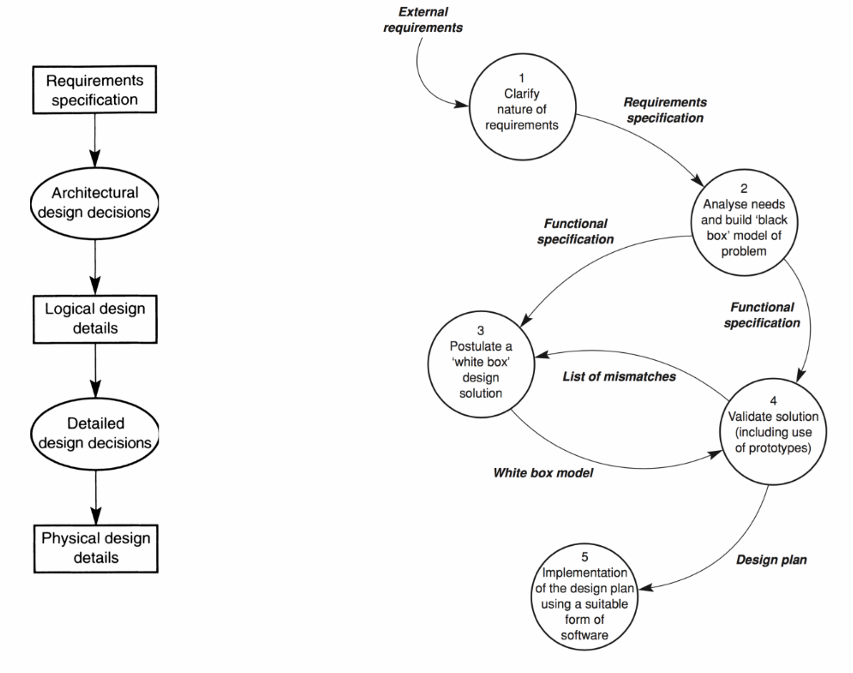
5.1 软件设计过程 Software Design Process
5.2 架构活动 Architecture Activities
- 为系统创建业务案例 Creating the business case for the System
- 理解需求 Understanding the requirements
- 创建和选择架构 Creating and selecting architecture
- 沟通架构(包括开发人员在内的涉众)
Communicating the architecture (stakeholders including developers) - 分析或评估架构 Analysing or evaluating the architecture
- 整体的方法论 Overall methodologies
- 具体技术的质量 Quality specific techniques
- 实现架构 Implementing the architecture
- 保证和架构的一致性 Ensuring conformance to an architecture
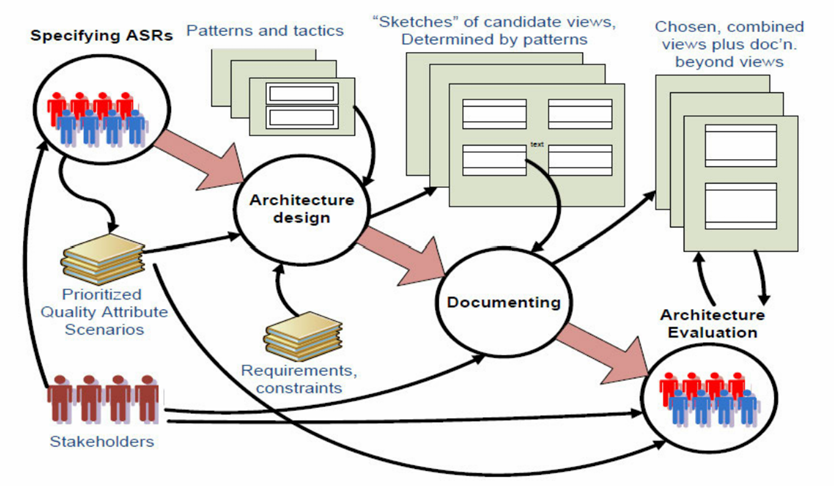
5.3 软件架构过程 Software Architecture Process
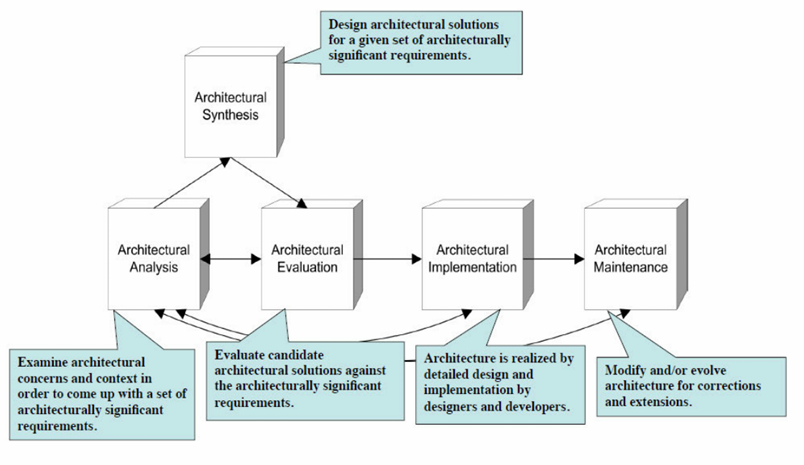
5.4 架构生命周期 Architecture Lifecycle
5.5 软件设计和架构知识领域 Software Design & Architecture Knowledge Areas
- 软件设计基本原理 Software Design Basic Concepts
- 整体设计原理 General design concepts
- 上下文: 软件发展生命周期 - 需求、设计、编码和测试
Context: software development life cycle - requirements, design, construction and testing - 设计过程: 角色、活动、工作产品 Design process(role, activity, work product)
- 软件设计的使能技术 Enabling techniques for software design
- 核心问题(技术): 一致性、事件控制和处理、分发、异常处理、交互系统、持久化
Key Issues (technical): concurrency, control and handling of events, distribution, exception handling, interactive systems, persistence - 软件结构和架构 Software Structure and Architecture
- 架构结构和观点 Architecture Structures and viewpoints
- 架构风格和模式(宏观架构) Architectural styles and patterns (macro-architecture)
- 设计模式(微观架构) Design patterns (micro-architecture)
- 软件设计方法 Software Design Methods
- 架构方法,比如属性驱动的设计 Architecture Methods (e.g., Attribute-Driven Design)
- 设计方法,比如动态系统发展方法 Design Methods (e.g., Dynamic System Development Method)
- 软件设计的质量分析和评估 Software Design Quality Analysis and Evaluation
- 质量属性 Quality attributes
- 质量分析和评估方法、技术和工具 Quality analysis and evaluation methods, techniques and tools
- 设计回顾: 比如SEI的架构权衡分析方法
Design reviews (e.g. SEI’s Architecture Trade-off Analysis Method) - 静态分析和动态分析 Static analysis and dynamic analysis
- 模拟和原型 Simulation and prototyping
- 设计回顾: 比如SEI的架构权衡分析方法
- 度量 Measures:
- 矩阵: 架构级别 Metrics: Architecture level
- 技术特有度量指标 Technique specific measures
- 设计建模和展示 Design Modeling and Representation
- 架构和设计符号(架构描述语言,ADL)
Architecture and Design Notations (Architecture Description Languages(ADL)) - 统一建模语言 Unified Modelling Language (UML)
- 设计文档(意见或其他) Design Documentation (Views & Beyond)
- 其他: 在活动、关注点和领域上的不同,比如 ACME,Rapide
Others: differ in ability, focus and domain (e.g. ACME, Rapide)
- 架构和设计符号(架构描述语言,ADL)
6. 讨论
- 科学和工程有什么不同?What is Difference between Science and Engineering?
- 科学的研究是研究这个世界既有的部分
- 工程是研究的是人类创造新的世界(是不是因为人才产生的)
- 软件和硬件有什么不同?What is Difference between ‘Software’ and ‘Hardware’?
- 软件是不可见的: 软件是虚拟的,而硬件是实体的。
- 软件制作出来就是为了被修改和改变的(软件的演化是他的本质属性)
- 架构和设计有什么不同?What is Difference between Architecture and Design?
- 所有的架构都是软件设计,但是不是所有的软件设计都是架构
- 架构是设计过程的一个过程。
- 其他观点
- 架构是更高层的设计,是为了修改的
- 架构是设计决策的组合
- 架构和结构有什么不同?What is Difference between Architecture and Structure?
- 架构定义了组件(Component)的接口,Component之间如何交流以及如何相互依赖,Component的职责。
- 架构提供了设计的更高层抽象视角,隐藏设计的复杂性和实现,更强调非功能性需求。
- 【标准】架构是包括结构信息的,因为结构是一种静态的、逻辑的、是关于系统如何构成。但是架构除了包含结构,还会增加组件的相互之间的关系接口,还会定义一些动态的行为(一个组件可能和谁进行交互)