1. AOP思想及术语
见服务端开发
2. Spring AOP基于注解方式实现
2.1 Spring AOP底层技术
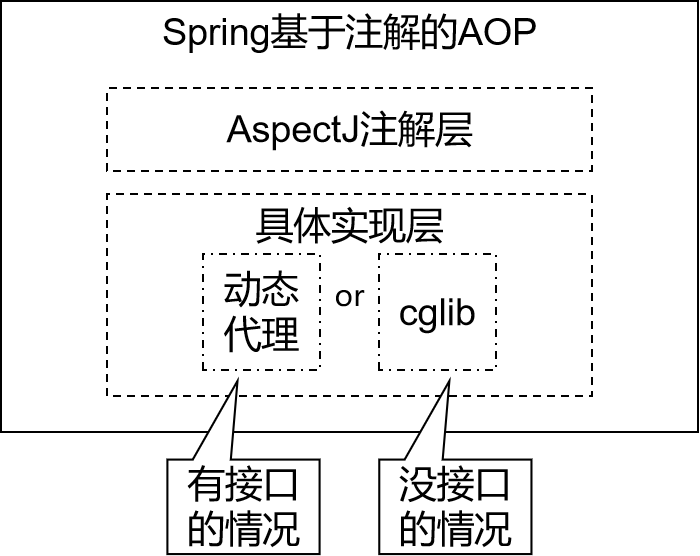
动态代理见Java动态代理
- JDK 动态代理:JDK原生的实现方式,需要被代理的目标类必须实现接口。因为这个技术要求代理对象和目标对象实现同样的接口
- cglib:通过继承被代理的目标类实现代理,所以不需要目标类实现接口
- AspectJ:早期的AOP实现的框架,Spring AOP借用了AspectJ中的AOP注解
2.2 示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Before(value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.proxy.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int,int))")
public void printLogBeforeCore() {
System.out.println("[AOP前置通知] 方法开始了");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.proxy.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int,int))")
public void printLogAfterSuccess() {
System.out.println("[AOP返回通知] 方法成功返回了");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.proxy.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int,int))")
public void printLogAfterException() {
System.out.println("[AOP异常通知] 方法抛异常了");
}
@After(value = "execution(public int com.atguigu.proxy.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int,int))")
public void printLogFinallyEnd() {
System.out.println("[AOP后置通知] 方法最终结束了");
}
}
|
开启 aspectj 注解支持
- XML方式:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
- 配置类方式:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
编写测试类及运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@SpringJUnitConfig(value = {MyConfig.class})
public class AopTest {
@Autowired
private Calculator calculator;
@Test
public void testCalculator(){
calculator.add(1,1);
}
}
|

2.3 获取通知细节信息
JoinPoint接口
需要获取方法签名、传入的实参等信息时,可以在通知方法声明JoinPoint类型的形参
- JoinPoint 接口通过
getSignature() 方法获取目标方法的签名(方法声明时的完整信息)
- 通过目标方法签名对象获取方法名
- 通过 JoinPoint 对象获取外界调用目标方法时传入的实参列表组成的数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
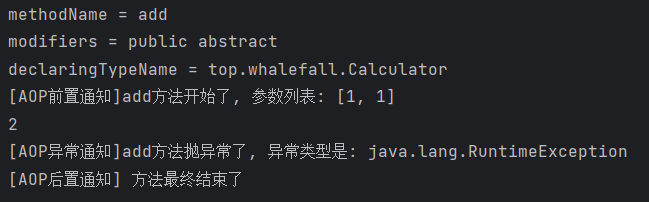
| @Before(value = "execution(public int top.whalefall.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int, int))")
public void printBeforeCore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String methodName = signature.getName();
System.out.println("methodName = " + methodName);
int modifiers = signature.getModifiers();
System.out.println("modifiers = " + modifiers);
String declaringTypeName = signature.getDeclaringTypeName();
System.out.println("declaringTypeName = " + declaringTypeName);
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("[AOP前置通知]" + methodName + "方法开始了, 参数列表: " + Arrays.asList(args));
}
|

注: 这里显示的是接口的方法签名
方法返回值
在返回通知中,通过 @AfterReturning 注解的 returning 属性获取目标方法的返回值
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int top.whalefall.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int, int))",
returning = "targetMethodReturnValue")
public void printLogAfterSuccess(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object targetMethodReturnValue) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[AOP返回通知]" + methodName + "方法成功返回了, 返回值是: " + targetMethodReturnValue);
}
|

异常对象捕获
在异常通知中,通过 @AfterThrowing 注解的throwing属性获取目标方法抛出的异常对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public int top.whalefall.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int, int))",
throwing = "targetMethodException")
public void printLogAfterException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable targetMethodException) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[AOP异常通知]" + methodName + "方法抛异常了, 异常类型是: " + targetMethodException.getClass().getName());
}
|
2.4 切点表达式
切点表达式语法
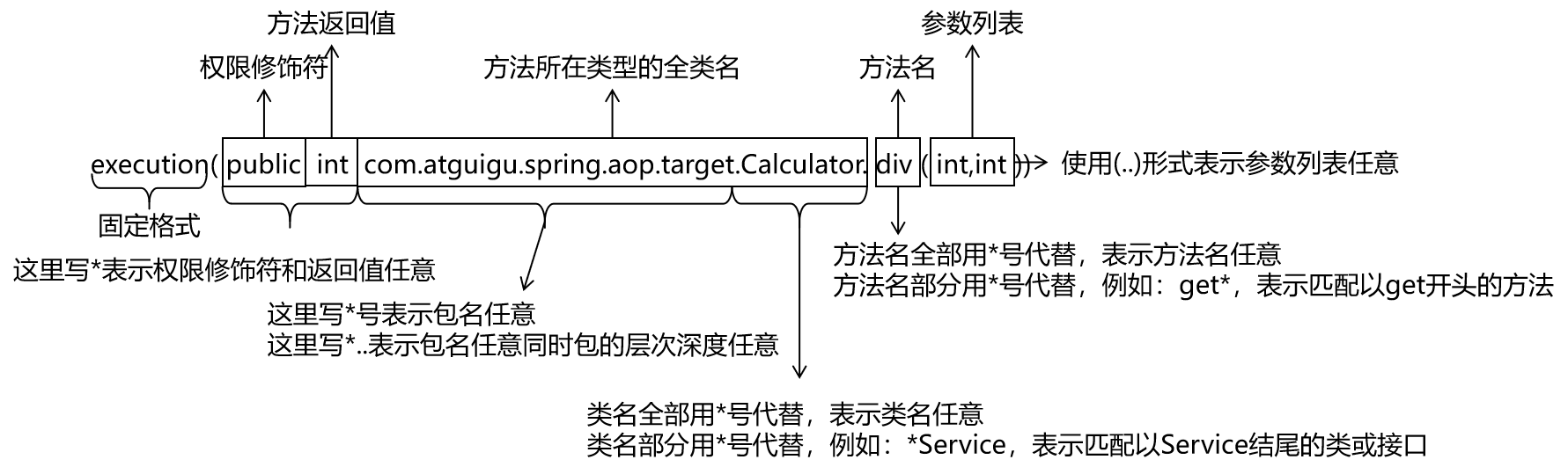
- 第一位:execution() 固定开头
- 第二位:方法访问修饰符
- 第三位:方法返回值
- 注:execution( ) 是错误语法
- execution(*) == 只要不考虑 返回值 或者 访问修饰符 相当于全部不考虑了
- 第四位:指定包的地址
*: 任意一层的任意命名..: 任意层, 任意命名, 不能用作包开头- 任何包使用
*..
- 第五位:指定类名称
*: 任意类名- 部分任意:
com..service.impl.*Impl
*..*: 任意包任意类
- 第六位:指定方法名称
- 语法与类名一致
- 任意访问修饰符, 任意类的任意方法:
* *..*.*
- 第七位:方法参数
- 模糊值: 任意参数 有 或者 没有 (..)
- 第一个参数是字符串的方法 (String..)
- 最后一个参数是字符串 (..String)
- 字符串开头, int结尾 (String..int)
- 包含int类型 (..int..)
重用切点表达式
同一类内部引用
1
2
3
4
5
| @Pointcut("execution(public int top.whalefall.CalculatorPureImpl.add(int, int))")
public void declarePointCut() {}
@Before(value = "declarePointCut()")
public void printBeforeCore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {...}
|
不同类中引用
只需要添加类的全限定符 + 方法名即可
1
2
| @Before(value = "top.whalefall.LogAspect.declarPointCut()")
public Object roundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {}
|
建议将切点表达式统一存储到一个类中进行集中管理和维护
2.5 环绕通知
@Around == @Before + @After == @Before + @AfterReturning + @AfterThrowing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
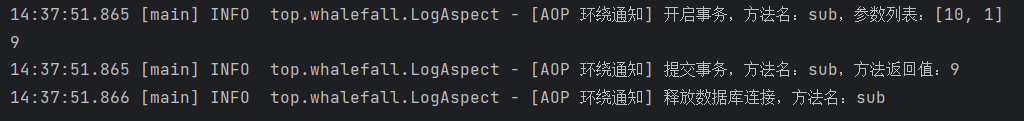
| @Around(value = "execution(public int top.whalefall.CalculatorPureImpl.sub(int, int))")
public Object manageTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Logger log = LogManager.getLogger(LogAspect.class);
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String methodName = signature.getName();
Object targetMethodReturnValue = null;
try {
log.info("[AOP 环绕通知] 开启事务,方法名:" + methodName + ",参数列表:" + Arrays.asList(args));
targetMethodReturnValue = joinPoint.proceed(args);
log.info("[AOP 环绕通知] 提交事务,方法名:" + methodName + ",方法返回值:" + targetMethodReturnValue);
}catch (Throwable e){
log.info("[AOP 环绕通知] 回滚事务,方法名:" + methodName + ",异常:" + e.getClass().getName());
}finally {
log.info("[AOP 环绕通知] 释放数据库连接,方法名:" + methodName);
}
return targetMethodReturnValue;
}
|
2.6 切面优先级设置
相同目标方法上同时存在多个切面时,切面的优先级控制切面的内外嵌套顺序。
使用 @Order 注解可以控制切面的优先级(用在类上):
@Order(较小的数):优先级高@Order(较大的数):优先级低
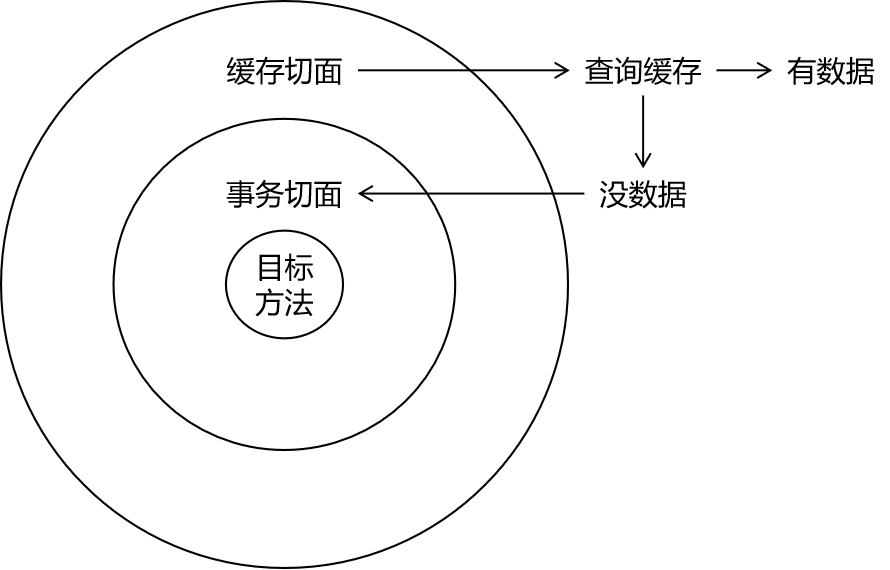
如果目标类有接口, Spring自动选择使用jdk动态代理
如果目标类没有接口, Spring自动选择cglib动态代理
3. Spring AOP基于XML方式实现
配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
<bean id="calculatorPure" class="com.atguigu.aop.imp.CalculatorPureImpl"/>
<bean id="logAspect" class="com.atguigu.aop.aspect.LogAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="logPointCut" expression="execution(* *..*.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logAspect">
<aop:before method="printLogBeforeCore" pointcut-ref="logPointCut"/>
<aop:after-returning
method="printLogAfterCoreSuccess"
pointcut-ref="logPointCut"
returning="targetMethodReturnValue"/>
<aop:after-throwing
method="printLogAfterCoreException"
pointcut-ref="logPointCut"
throwing="targetMethodException"/>
<aop:after method="printLogCoreFinallyEnd" pointcut-ref="logPointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
|
4. Spring AOP对获取Bean的影响
| 有无接口 |
实现类个数 |
有无切面 |
根据接口获取bean |
根据类获取bean |
| 有 |
1 |
无 |
可以 |
可以 |
| 有 |
多个 |
无 |
不可以 |
可以 |
| 有 |
1 |
有 |
可以 |
不可以,容器中的是代理类的对象 |
| 无 |
1 |
有 |
|
可以,cglib通过继承生成的代理类 |







