课程主页 :https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2021/schedule.html
虚拟机使用VMware Workstation 16 Player ,系统采用ubuntu20.04
安装必要工具
1 sudo apt-get install git build-essential gdb-multiarch qemu-system-misc gcc-riscv64-linux-gnu binutils-riscv64-linux-gnu
测试安装
Lab1 Xv6 and Unix utilities 1.1 Boot xv6 (easy) clone仓库并切换到util分支
1 2 3 $ git clone git://g.csail.mit.edu/xv6-labs-2021cd xv6-labs-2021
提交代码, -a 表示不需要git add 直接提交
1 2 'my solution for util lab exercise 1'
查看代码变动
1 2 3 4
启动qemu
查看可执行程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 $ ls cat 2 4 24256echo 2 5 23080kill 2 9 23024ln 2 10 22880ls 2 11 26448mkdir 2 12 23176rm 2 13 23160wc 2 18 25344
xv6没有ps命令,但按Ctrl-p,内核会打印每个进程的信息。如果现在尝试,会看到两行
退出可按住Ctrl-a,再输入x
通过make grade获取成绩,make handin提交lab
1.2 sleep (easy) user中创建sleep.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include "kernel/types.h" #include "kernel/stat.h" #include "user/user.h" int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {if (argc < 2 ) {fprintf (2 , "Please enter a number!\n" );exit (1 );1 ]));exit (0 );
添加到Makefile中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 UPROGS=\
测试
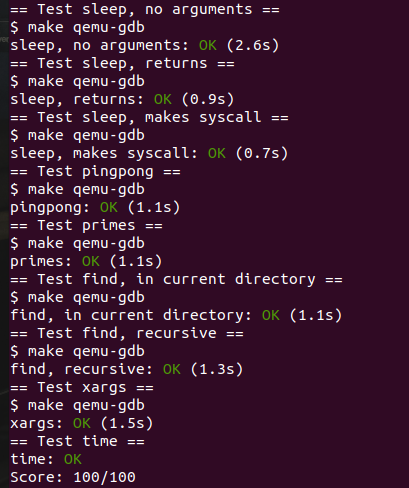
1 2 3 4 5 $ ./grade-lab-util sleep sleep , no arguments == sleep , no arguments: OK (2.1s) sleep , returns == sleep , returns: OK (0.6s) sleep , makes syscall == sleep , makes syscall: OK (0.9s)
1.3 pingpong (easy) 添加到Makefile
user中添加pingpong.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include "kernel/types.h" #include "kernel/stat.h" #include "user/user.h" #define READEND 0 #define WRITEEND 1 int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {int p1[2 ];int p2[2 ];int pid;char buf[1 ];if (pid < 0 ) {exit (1 );else if (pid == 0 ) {1 );printf ("%d: received ping\n" , getpid());1 );exit (0 );else {" " , 1 );1 );printf ("%d: received pong\n" , getpid());exit (0 );
使用两个管道进行双向的数据传输,子进程要先等待父进程写才能读,之后父进程要等子进程写才能读
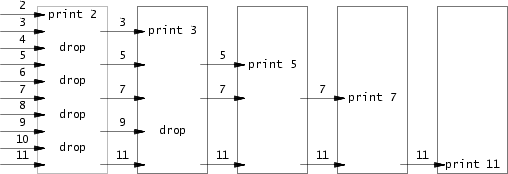
1.4 primes (moderate)/(hard) 素数筛法:将一组数feed到一个进程里,先print出最小的一个数,这是一个素数,然后用其他剩下的数依次尝试整除这个素数,如果可以整除,则将其drop,不能整除则将其feed到下一个进程中,直到最后打印出所有的素数。
解决思路:采用递归,每次先尝试从左pipe中读取一个数,如果读不到说明已经到达终点,exit,否则再创建一个右pipe并fork一个子进程,将筛选后的数feed进这个右pipe。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include "kernel/types.h" #include "kernel/stat.h" #include "user/user.h" #define READEND 0 #define WRITEEND 1 void child (int *p) ;int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {int p[2 ];if (fork() == 0 ) {else {for (int i = 2 ; i <= 35 ; i++) {sizeof (int ));0 );exit (0 );void child (int * p) {int pr[2 ];int n;if (read(p[READEND], &n, sizeof (int )) == 0 ) {exit (0 );if (fork() == 0 ) {else {printf ("prime %d\n" , n);int prime = n;while (read(p[READEND], &n, sizeof (int ))) {if (n % prime != 0 ) {sizeof (int ));0 );exit (0 );
1.5 find (moderate) 模仿 ls.c 即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include "kernel/types.h" #include "user/user.h" #include "kernel/fs.h" #include "kernel/stat.h" #include "kernel/fcntl.h" void find (char *path, char * file) ;int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {if (argc != 3 ) {fprintf (2 , "find: You need pass in only 2 argument" );exit (1 );char *target_path = argv[1 ];char *target_file = argv[2 ];exit (0 );void find (char *path, char * file) {char buf[512 ], *p;int fd;struct dirent de ;struct stat st ;if ((fd = open(path, 0 )) < 0 ){fprintf (2 , "find: cannot open %s\n" , path);return ;if (fstat(fd, &st) < 0 ){fprintf (2 , "find: cannot stat %s\n" , path);return ;switch (st.type){case T_FILE:if (strcmp (path + strlen (path) - strlen (file), file) == 0 ) {printf ("%s\n" , path);break ;case T_DIR:if (strlen (path) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf){printf ("find: path too long\n" );break ;strcpy (buf, path); strlen (buf);'/' ;while (read(fd, &de, sizeof (de)) == sizeof (de)){if (de.inum == 0 )continue ;0 ;if (stat(buf, &st) < 0 ){printf ("find: cannot stat %s\n" , buf);continue ;if ((strcmp (de.name, "." ) != 0 ) && (strcmp (de.name, ".." ) != 0 )) {break ;
1.6 xargs (mederate) 实现将标准输入作为参数一起输入到xargs后面跟的命令中,比如
1 2 $ echo hello too | xargs echo bye bye hello too
如果标准输入有多行,那么也要执行多次命令
使用fork起一个子进程,在子进程中用exec执行相应的命令。父进程wait。对标准输入每次读一个char,若读到\n需要执行命令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include "kernel/types.h" #include "user/user.h" #include "kernel/param.h" #define MAX_LEN 100 int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {char *command = argv[1 ];char bf;char paramv[MAXARG][MAX_LEN]; char *m[MAXARG];while (1 ) {int count = argc - 1 ; memset (paramv, 0 , MAXARG * MAX_LEN);for (int i = 1 ; i < argc; i++) {strcpy (paramv[i - 1 ], argv[i]);int cursor = 0 ; int flag = 0 ; int read_result;while (((read_result = read(0 , &bf, 1 ))) > 0 && bf != '\n' ) {if (bf == ' ' && flag == 1 ) {0 ;0 ;else if (bf != ' ' ) {1 ;if (read_result <= 0 ) {break ;for (int i = 0 ; i < MAXARG - 1 ; i++) {1 ] = 0 ; if (fork() == 0 ) {exit (0 );else {int *) 0 );exit (0 );
到这里lab1就全部完成了!